The 4:3 aspect ratio was one of the earliest standards used, often called the "classic" or "standard" ratio. It means that for every 4 units of width, there are 3 units of height, giving the screen a somewhat square look compared to modern wide screens.
Please read our article: Screen Aspect Ratio Calculator
What are the 4:3 resolutions?
When we talk about the 4:3 aspect ratio, a handful of popular resolutions come to mind. These resolutions played a major role during the 1990s and early 2000s and are still recognized today:
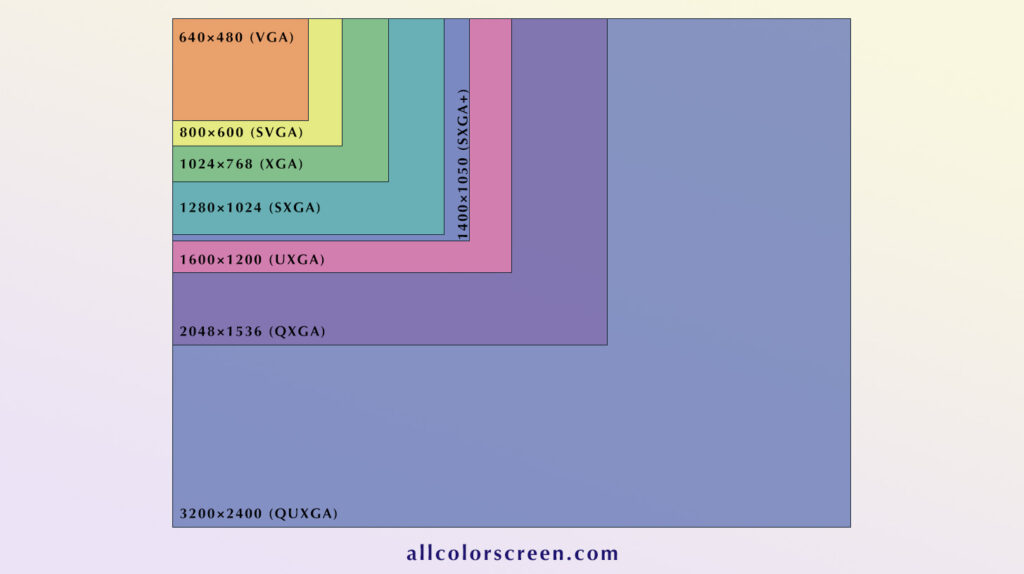
- 640x480 (VGA): The earliest and most widely used resolution for early PC monitors and televisions. It is commonly associated with classic games and early Windows operating systems.
- 800x600 (SVGA): A step up from VGA, this resolution was prevalent in the 1990s and 2000s for business PCs and home computing. It offered a clearer and more detailed display.
- 1024x768 (XGA): One of the most popular 4:3 resolutions during the rise of home computing and business projectors. Many office computers in the 2000s used this resolution.
- 1152x864: This resolution provided a small bump in clarity over 1024x768 and was occasionally found on high-end CRT monitors. It offered a slightly larger workspace for professional tasks.
- 1280x960: A higher-quality 4:3 resolution often used for detailed applications like image editing, gaming, and video playback on larger CRT monitors.
- 1280x1024 (SXGA): Although technically a 5:4 ratio, this resolution is often mentioned alongside 4:3 resolutions due to its common use on older monitors, especially for graphic design and CAD work.
- 1400x1050 (SXGA+): An enhanced version of SXGA, this resolution was popular with business-class laptops and desktop monitors that required more screen real estate without moving to widescreen.
- 1600x1200 (UXGA): This was one of the highest resolutions available for 4:3 displays. It was frequently used in graphic design, video editing, and other professional environments where clarity and workspace were essential.
- 1856x1392: A less common resolution that offered even more screen real estate for professionals working in media production or high-end computing applications.
- 1920x1440: Another higher-end resolution for 4:3 displays, offering sharp and detailed imagery. It was mainly used in specialized fields like design and medical imaging.
- 2048x1536 (QXGA): One of the highest resolutions ever produced for 4:3 aspect ratio monitors. It was used for ultra-high-definition displays and specific professional applications such as video editing, medical analysis, and CAD work.
- 2560x1920: A rare resolution that delivered extreme clarity and was typically reserved for large, high-end CRT monitors used in scientific and technical applications.
- 3200x2400 (QUXGA): Among the highest resolutions ever made for 4:3 monitors. This was primarily used in very specialized fields like medical imaging, scientific research, and other industries that required extremely high-resolution displays.


